If you’re an organic gardener in a tropical climate, the chances are you’ve asked yourself this question more than once. Rest assured that the process of growing your own banana trees (and harvesting them) isn’t too complicated or time-consuming!
Young banana trees typically bear fruit about 10-20 months after planting. Trees are first planted as 2″-6″ wide suckers divided off a mother plant. The suckers grow for about a year before they send up a flower stalk. Banana trees usually bloom in May-July in the southern US, and it then takes 3-4 months for the fruits to develop. Certain varieties take longer to mature.
Read on to learn more about when banana trees start to bear fruit!
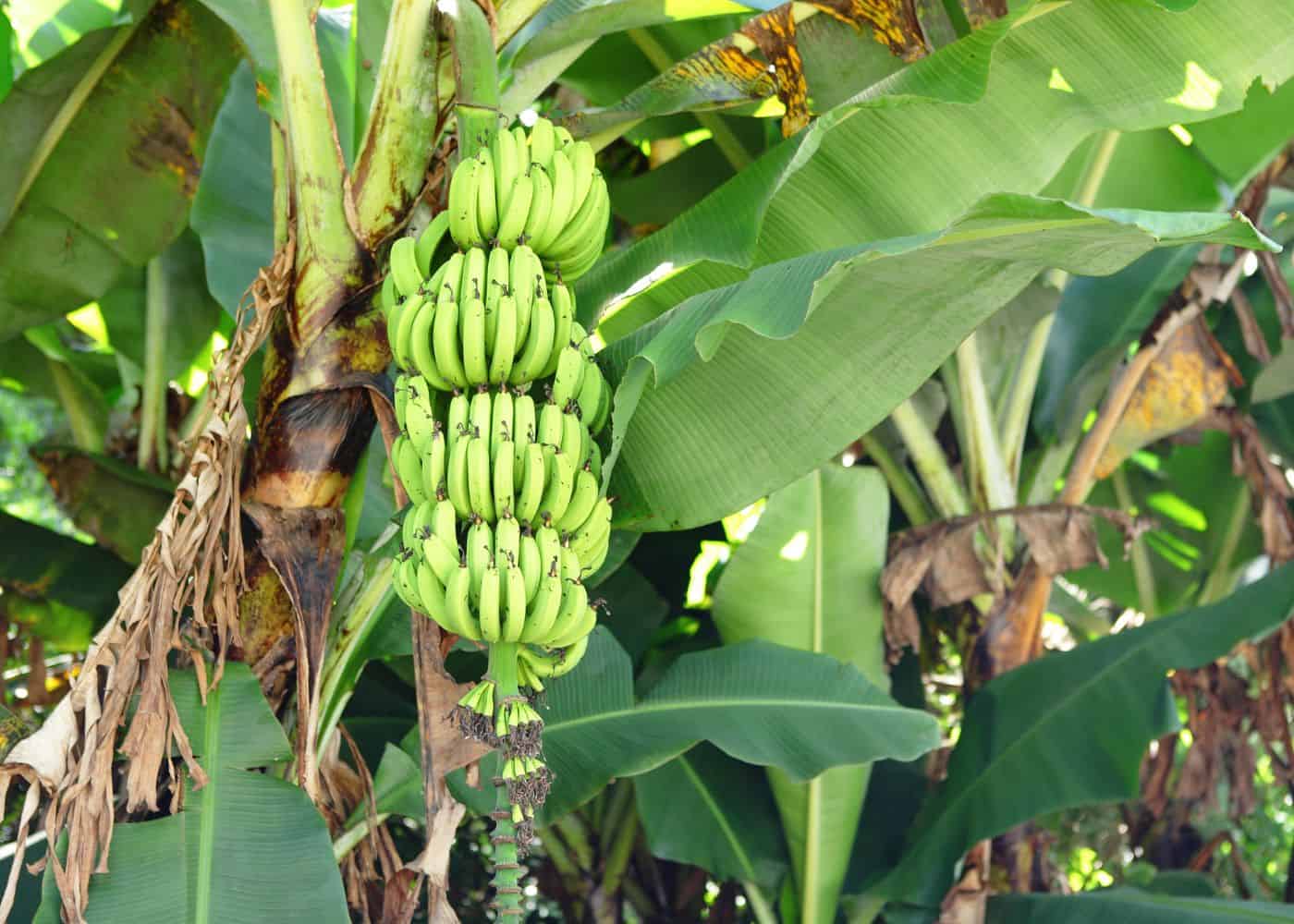

When do banana trees produce ripe bananas?
Young banana trees typically bear fruit about 10-20 months after planting. Most banana trees are not grown from seeds, and are instead divided off of an older plant. Banana plants form mats of underground rhizomes which periodically send up suckers.
Narrow suckers can be divided off the main plant with a sharp spade and potted up as individual baby plants. Choose narrow-leaved suckers with a stem about 2″-6″ wide if possible for the quickest time to harvest. The best time to divide a banana plant is in the spring, but these plants quite tolerant to division.
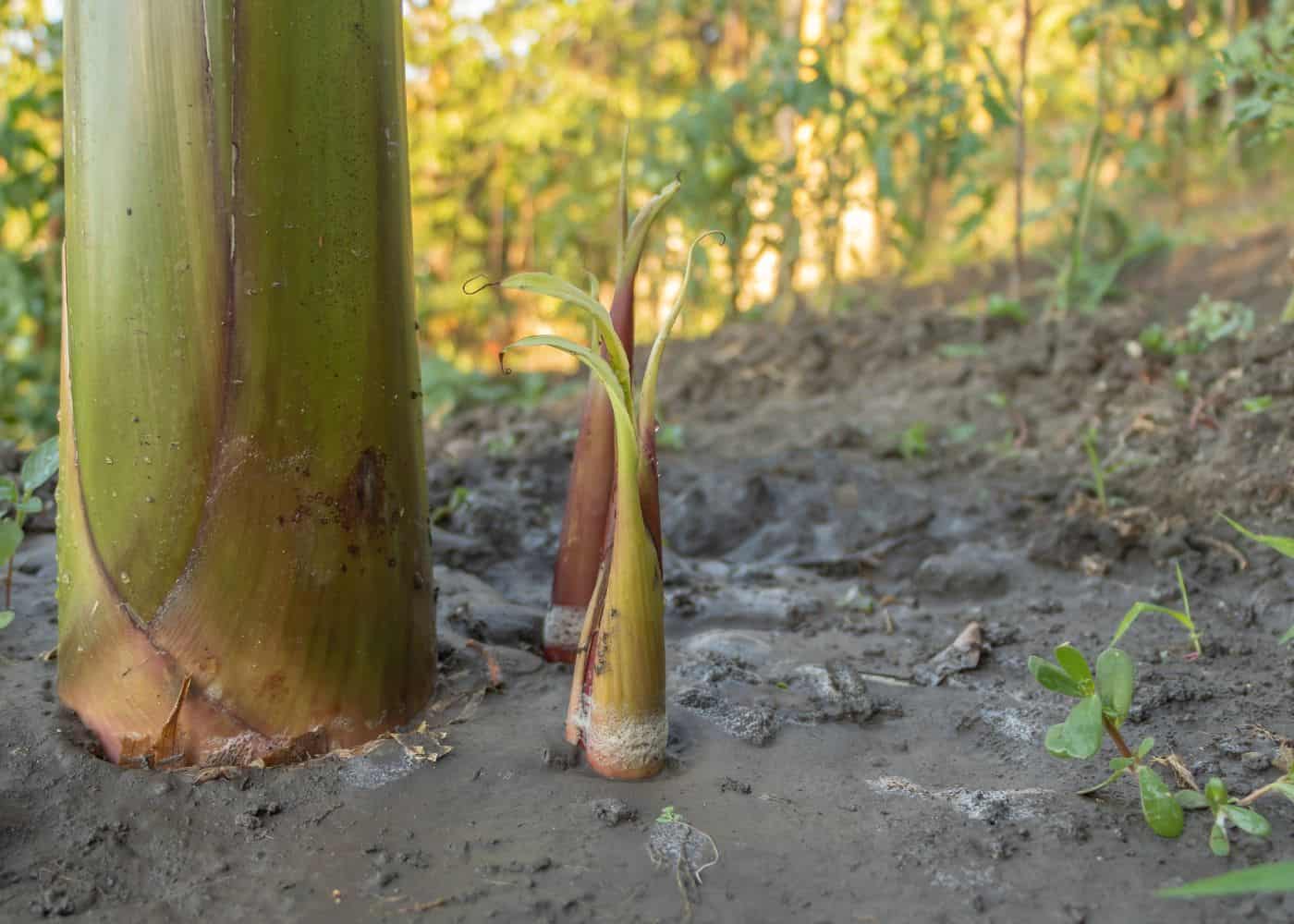

New divisions usually grow for about a year before they flower and set fruit. During this time the banana trees grow rapidly, especially if they have optimal soil, sunlight, temperature, and space conditions.
Banana trees usually bloom in May-July in the southern US. It takes 3-4 months for banana flowers to grow to mature fruits, with some large varieties taking 5-6 months in certain conditions.
“Most bananas will produce the flower bud within 10 to 15 months of emergence as a new sucker, depending mostly on variety and extent of cool/cold weather. Most production north of the lower Rio Grande Valley occurs in the spring and summer following a particularly mild winter.”
Texas A&M, Fruit & Nut Production
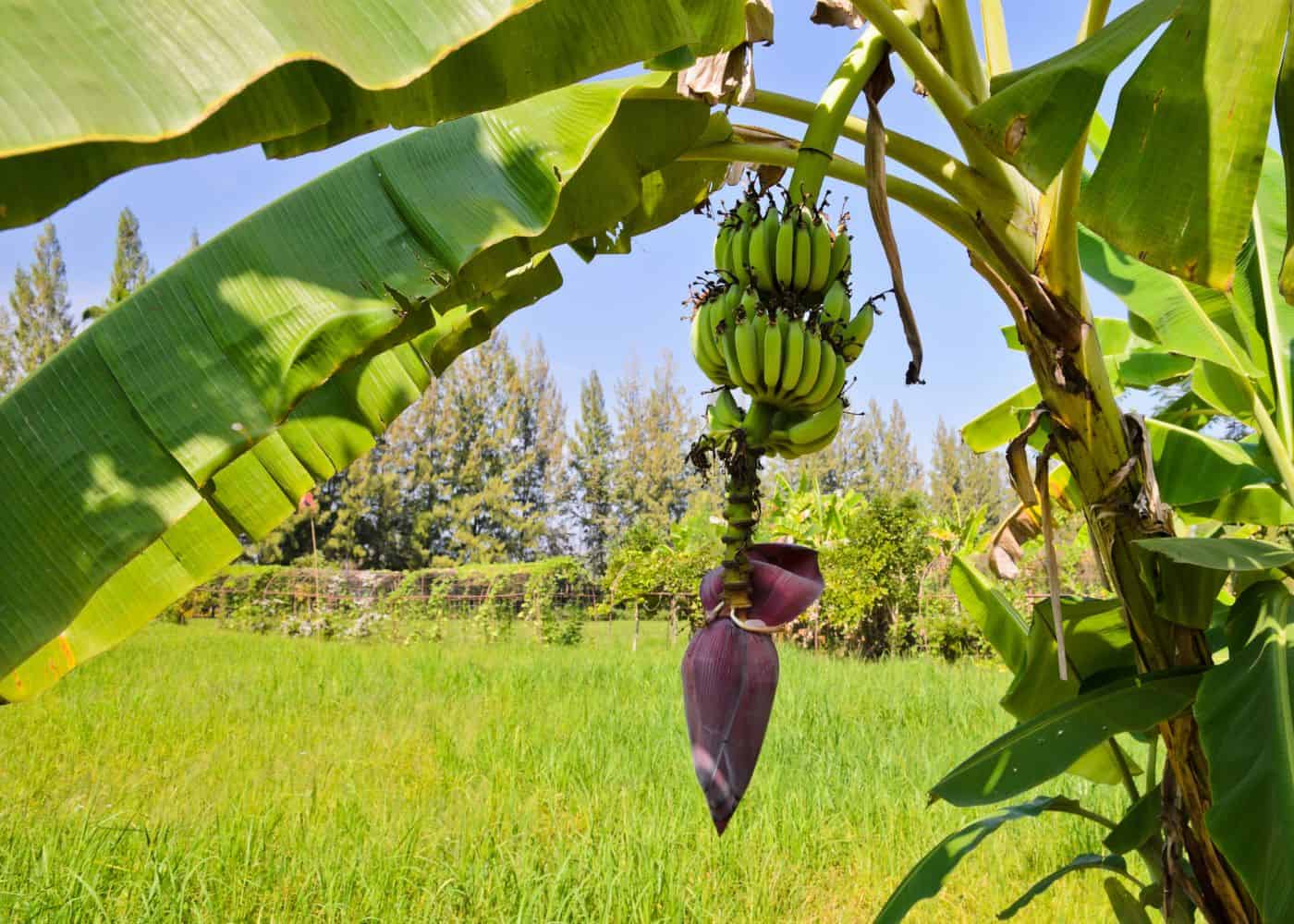

Choosing your banana tree
If you’re a fan of growing tropical plants, like banana trees, ensure you choose the right tree. Not every banana plant yields edible fruit, so you need to pick a banana plant bred to produce delicious fruit when selecting one. Some types, including red banana, dwarf banana, and pink velvet, are grown for their banana flowers rather than their fruit.
Planting banana trees
According to the University of Florida, banana plants will thrive when planted in healthy, wet soil in a wind-protected area. Apply fertilizer to young plants every two months, increasing this amount during the flowering and fruiting seasons. Bananas need about an inch or two of water per week.
Banana trees planted for their fruit are usually planted about 8-10 feet apart. Banana planted for ornamental purposes are generally planted much more closely – as close as 2-3 feet apart.
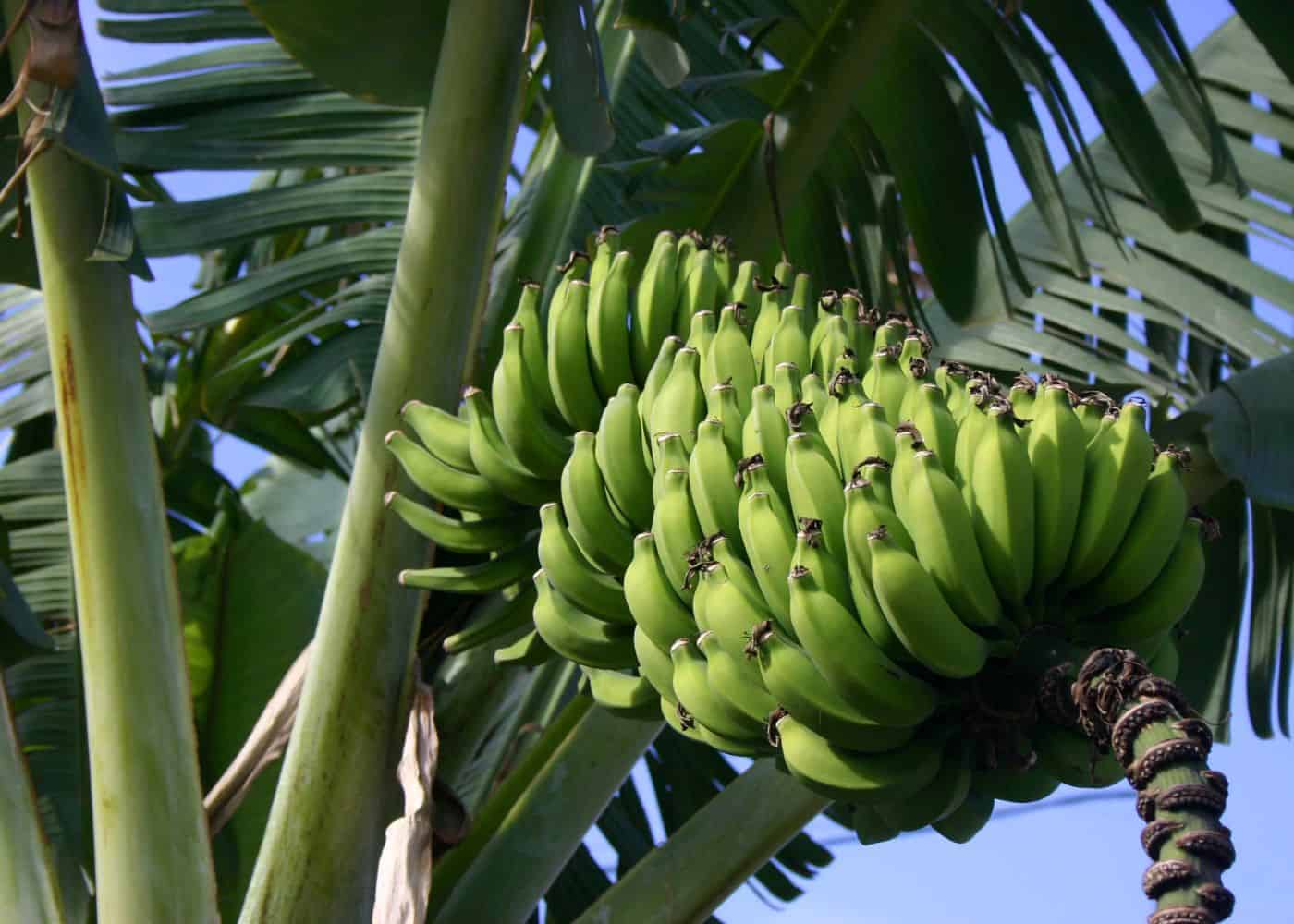

Growing banana trees for production
Banana trees have large underground root systems called rhizomes that shoot up multiple stalks. Try to keep each plant to 3-4 stalks at a time, with each stalk at a different growth stage.
Keep the oldest, tallest stalk as the fruiting stalk that grows the bananas. The next largest stalk is usually 1-4 feet tall, and is called a “sword sucker” if it has narrow leaves. This sucker will be the next fruiting stalk.
Then leave one or two narrow “peepers” (suckers) that are under about 2 feet tall. Remove tall weak stalks with broad leaves (water suckers), as they don’t tend to produce as well.
“A key feature is the banana’s rhizomatous root system, which puts up new stalks each year. For good fruit production, it helps to limit the plant to three or four stalks that are different ages. The oldest and tallest one should be flowering and/or fruiting. The second one should be one-half to one-third the size of the first. And finally, there should be one or two young plants that are six inches to three feet tall.”
Gardening Solutions, University of Florida
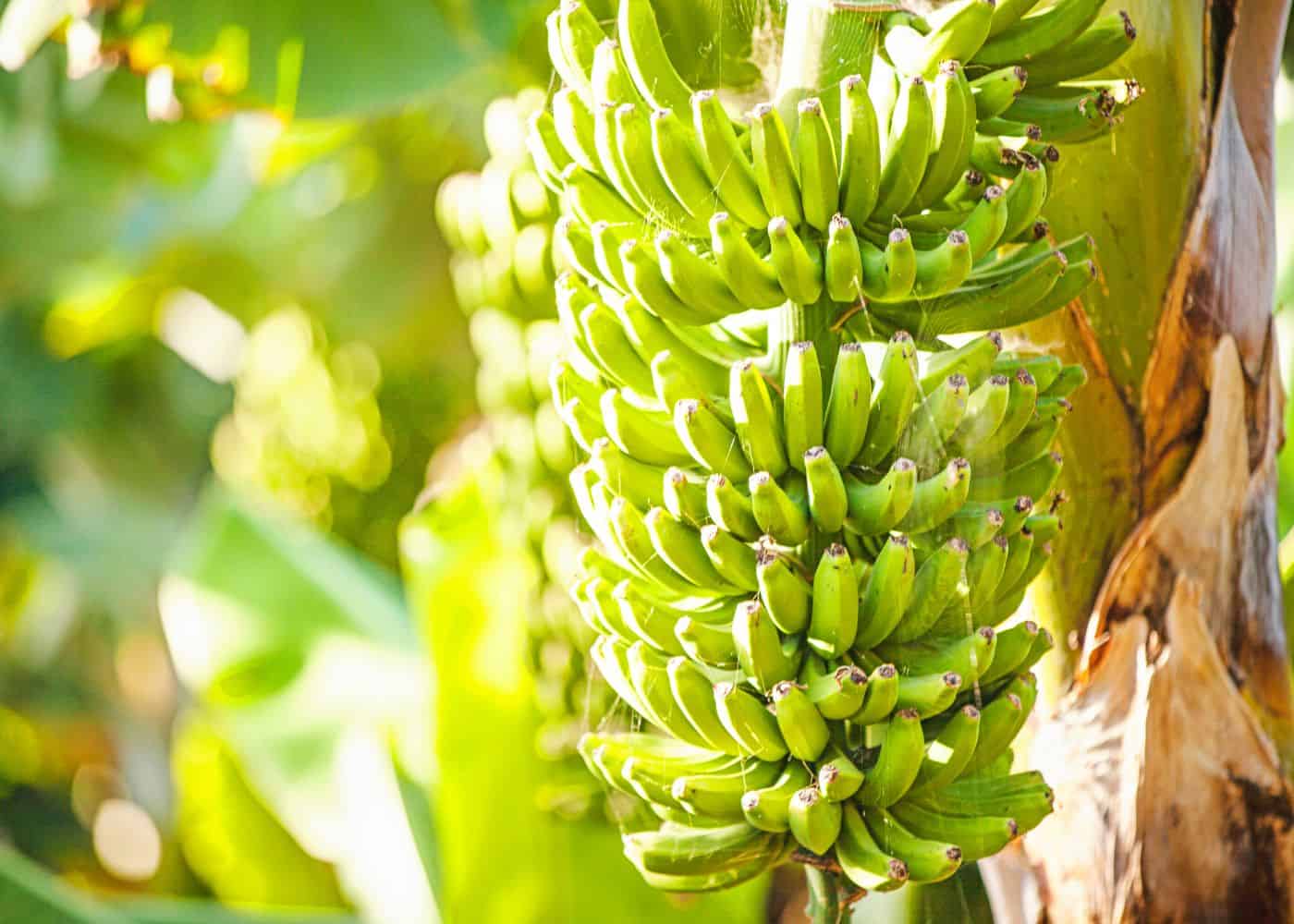

How much sun does a banana tree need?
Bananas grow best with at least six hours of sunlight. Try to plant them somewhere they get 6-8 hours of direct sunlight each day.
Although bananas are tropical plants and need direct sunlight, they may also be grown in areas with up to 50% shade. But it’s challenging to grow a banana plant in partial shade since too little sunlight may cause it to take longer to produce fruit.
Harvesting bananas
Various environmental factors will affect the plant’s exact time to harvest bananas. But if you supply the banana tree with what it needs, it will produce tasty fruit for you.
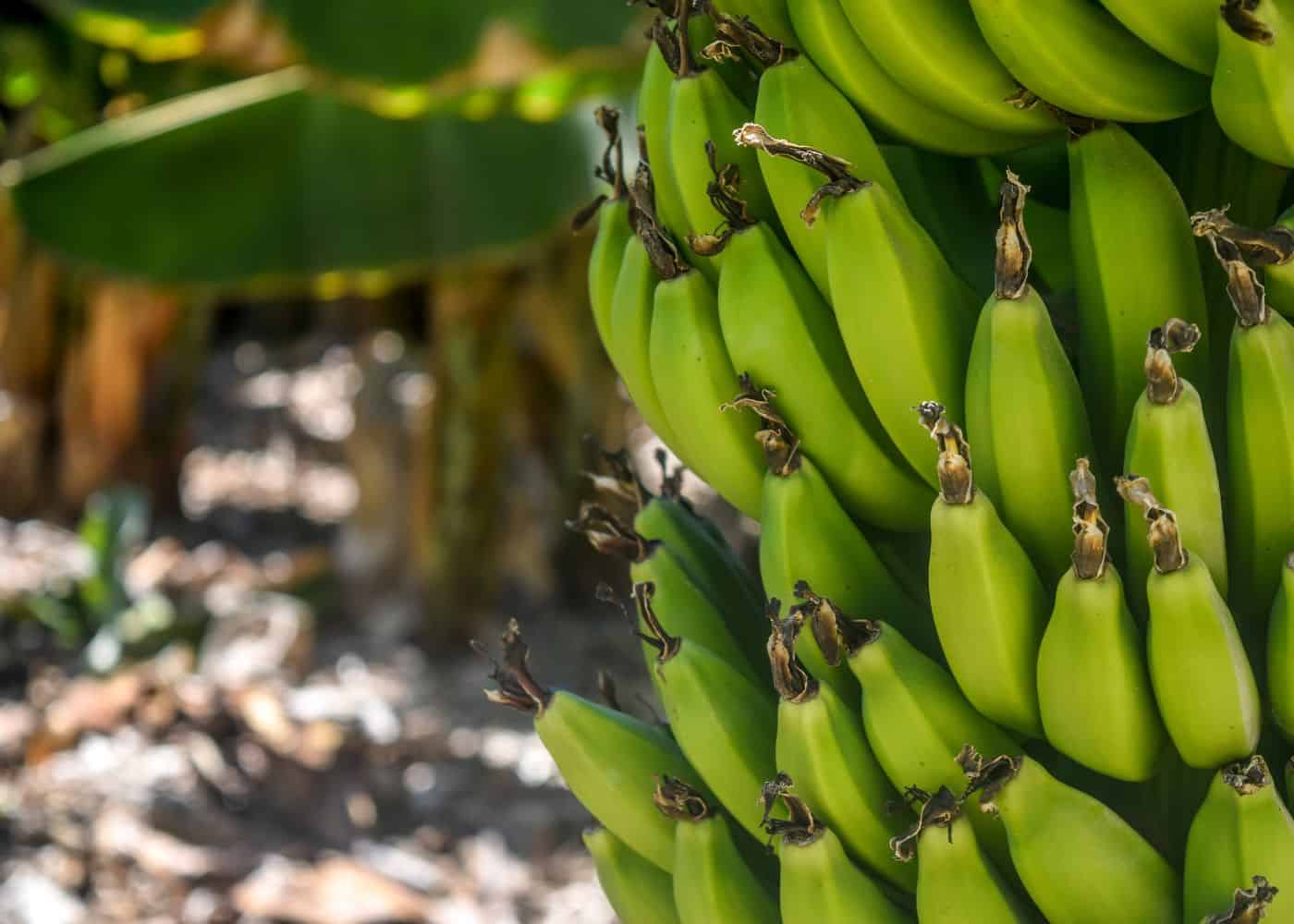
When the bananas get bigger and rounder in appearance, they are usually mature. Chop the entire stalk of ripe, green bananas off to harvest the bananas. Avoid letting them get yellow on the plant because they may break open and rot. Cut the entire stalk off when the fruits in the bunch are ready, then hang it in a dark area to let the fruit ripen and become yellow.
Whether it is mature or not, clip the stem and bring it inside if frosty. Despite their small size, the fruits should still ripen. Then, cut down the stem your fruit was growing on once you have harvested it. Cutting down a stem allows room for other stems to emerge because each one can only yield one bunch of bananas.
Take care when cutting your banana stalks. Banana fruit may not ripen the following summer if a stem gets cut in the fall. Only clip fruit-bearing stems.

Cold weather, pests, and other banana tree issues
Bananas are tropical fruit. The trees grow in warm, humid climates and can be sensitive to cold weather. Although a banana plant may withstand cold temperatures as low as 50 degrees Fahrenheit, it will not develop or bear fruit.
According to the New Mexico State University, temperatures below freezing can easily kill the plant. The middle of the 80s is the best temperature for a banana fruit set. If you live in an area with strong winds, consider a fence around the banana tree to protect it.
“Chilling damage and irreversible freeze damage may occur at or below 32°F (0°C). Symptoms of freeze damage include a water-soaked appearance to all above ground parts of the banana plant and desiccation, browning, and death of leaves, pseudostems, and fruit. Temperatures below 28°F (-2°C) may kill plants to the ground. However, new growth usually sprouts from the underground rhizome with the return of warm weather.”
University of Florida, Banana Growing In The Florida Home Landscape
Conditions of drought are also difficult for banana plants. Choking or extreme dryness can prevent the fruit from developing on the plant. Therefore, it’s crucial to continue watering your banana plant, especially in dry weather. According to the University of Arkansas Division of Agriculture, when temperatures drop, wrap plants and store them inside where they will not freeze and produce new fruit.

References
- University of Florida, Gardening Solutions
- Texas A&M, Fruit & Nut Production
- New Mexico State University, Growing Bananas in New Mexico
- University of Arkansas, Plant of the Week: Bananas