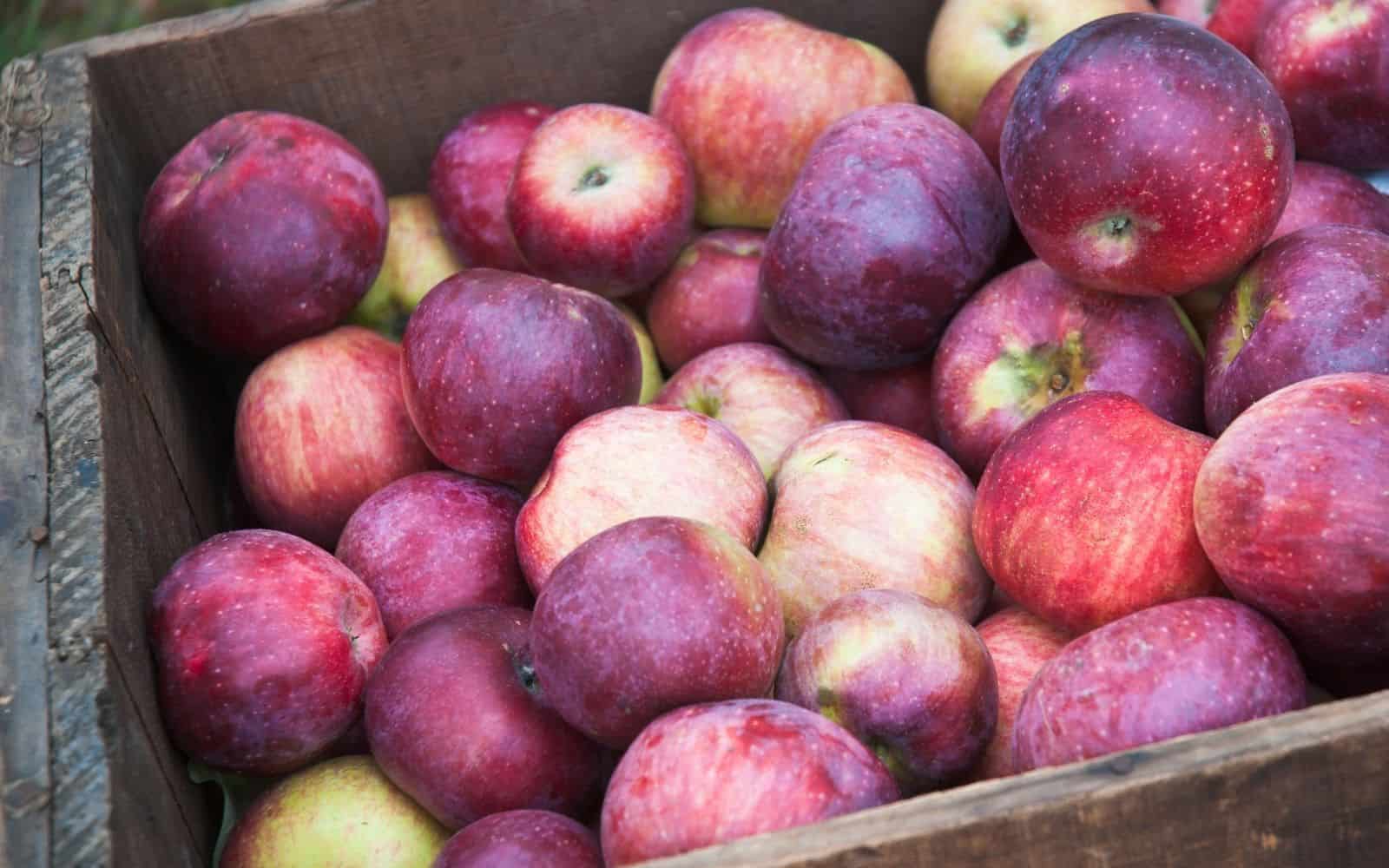
The Macoun apple is an American heritage variety known for its beautiful peel and creamy fresh apple taste. This medium-sized apple has a deep red-purple peel color with a bit of green, and is often shaped irregularly. The flesh is a creamy white color with a delicious hint of berry flavor.

Macoun apple basics
Macoun apples, known for their sweet and slightly tart flavor, are a favorite for fresh eating. This is one of the best seasonal specialty apples from the northeast. Macoun is known for its bright sweet-tart effervescent taste and incredibly fine and light texture.
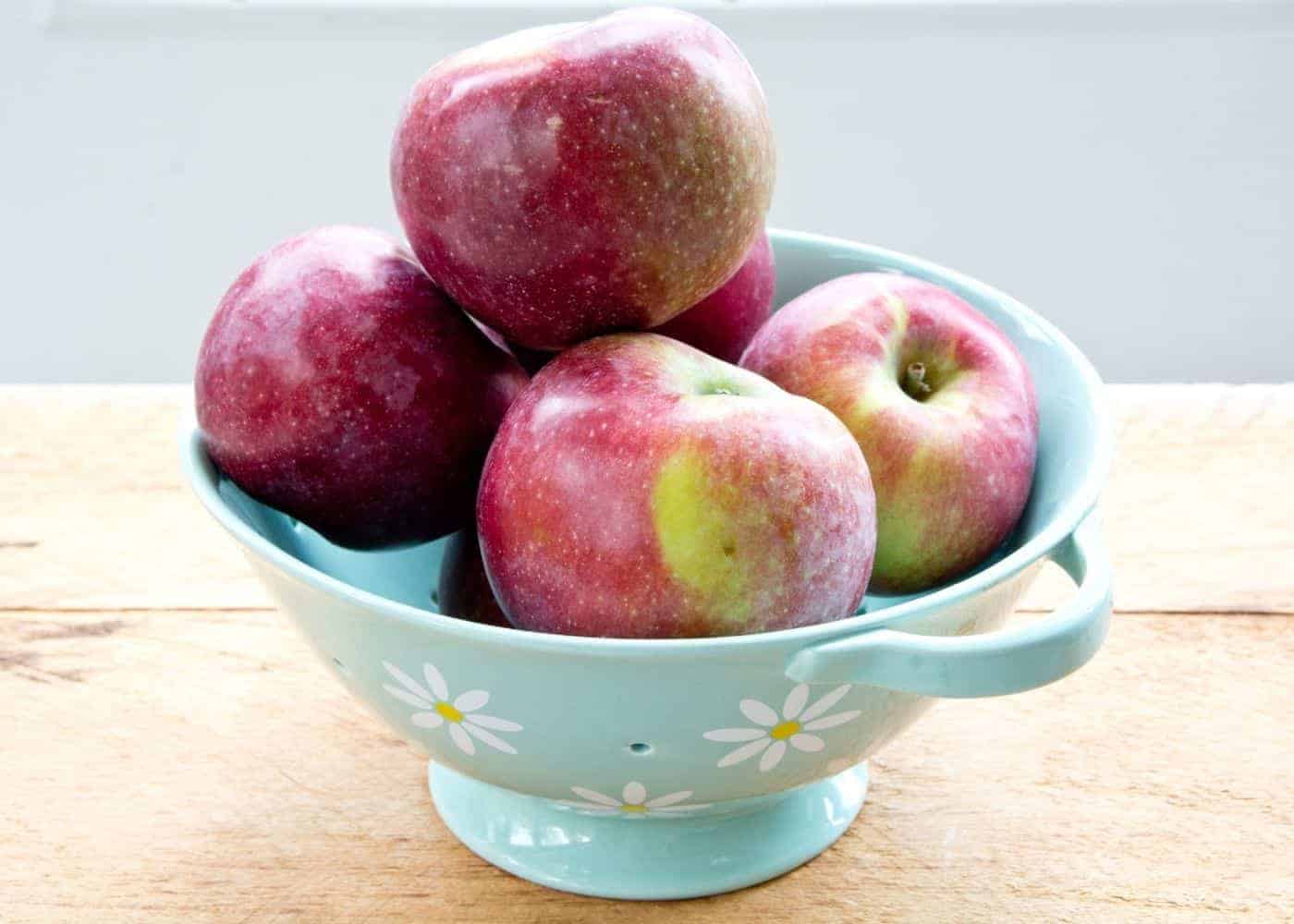
The peel is a dark burgundy-red tone, while the flesh inside is snow white. The Macoun apple was developed in 1923 at the New York State Agricultural Experiment Station in Geneva. This cultivar was grown from a McIntosh seedling.
This apple has darker skin than more common types of apples and it might even give off a purplish hue at times. It gets this dark skin from one of its parent cultivars, Jersey Black, and the tart, smooth flesh from the other parent: McIntosh. Macoun is a medium-sized apple and is about 2 and 3/4 inches in diameter.
It also tastes great! It has a sweet and slightly tart flavor that is packed into a crispy bite. There is also a faint berry-like flavor to the Macoun, which many people love. These apples were created with the intent to be eaten fresh. They are the tastiest when they are picked right off the tree, as they become soft quickly in storage after picking.
Origins of the Macoun apple
Macoun was bred by Richard Wellington in 1923 at the New York State Agricultural Experiment Station in Geneva. The cultivar is named after Canadian horticulturalist W. T. Macoun.
Since its beginnings, Macoun has become more widely accepted as an apple that can also be used for baking, even though its original creation was intended for snacking and fresh eating.
“This great apple – the best thing to ever spring from a McIntosh seed – might have conquered the nation ninety years before Honeycrisp if only it had been named something like Purple Haze. Instead, it has flown under the radar, filling the baskets of apple insiders while struggling in the market”
Apples of Uncommon Character: Heirlooms, Modern Classics, and Little-Known Wonders, by Rowan Jacobsen

Growing regions
Macoun apples are mainly grown in the northeast. They grow best in New York, New England, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Vermont, and Rhode Island. Macouns that are grown in southern areas often lack the characteristic crunchy texture.
These cooler states have become the best place to grow Macoun apples because of the cool nights. The daily temperature differential helps the fruits to grow properly and retain their flavor and texture. Cool nights also help it develop that dark red-purple peel hue.
Harvest season
Macoun apple’s harvest season is generally from mid-September to mid-October. Timing also varies due to the weather in the autumn, with cooler nights needed for the fruit to develop its characteristic color and texture on the tree.
The season for this apple is quite a small window. Many people in the areas where it is grown will wait around for it patiently because it comes and goes so fast that you are bound to miss the window if you are not careful.
This apple is by far the best when freshly picked. Harvested fruits grown in the north will keep for a week or two before becoming soft, but southern-grown fruits become mealy almost immediately.
With their short shelf life, it is best to use or eat them within a few days of picking them. This will help them to better retain their taste and crispness. After all, no one wants a squishy, mealy apple!
If needed, they can last for about 2 weeks in a refrigerated area. It is also suggested that you do not wash the apple until right before you eat it because this allows it to keep its natural protective coating for as long as you have it stored.

How to grow Macoun apples
Macoun apple trees grow best in the northeastern states and other similar climates with cool nights and cold winters. They can be grown in hardiness zones 4-8, but the flavor is best in zones 4-6.
A Macoun Apple tree will need a growing partner for effective blossom pollination. These mid to late-season bloomers flower alongside many popular varieties, so finding a nearby apple or crabapple tree is often quite easy. Good pollinating partners for Macoun include Honeycrisp, Gala, Fuji, and Granny Smith.
Choose a location with full sun (at least 6 hours of direct sunlight daily) and well-drained soil. Ensure the soil is fertile and well-draining by digging a small test hole and pouring in some water to make sure it drains out easily. You can also test the soil pH (it should be between about 6.0 and 7.0). Amend the soil with organic matter and any other necessary ammendments to improve fertility and drainage if needed.
Plant in early-mid spring, but before the heat of summer sets in. You can also plant these trees quite successfully in early fall when the soil is still warm but the nights are starting to cool off.
Dig a hole twice as wide and just as deep as the root ball. Carefully unfurl any thick circling roots around the rootball. Place the tree in the hole, ensuring the graft union lump (where the scion meets the rootstock) is above the soil line. Backfill the hole with soil and water thoroughly.
Water the new tree regularly, especially during the first few years. Later on, you’ll also want to water the established tree in dry periods. Macoun apple trees need about 1 inch of water per week, either from rainfall or irrigation.
If there are wide temperature fluctuations in your area, you may consider painting the bottom few feet of the trees trunk with whitewash to decrease the chance of bark splitting on a sunny, cold day. Prune the young tree in late winter to remove dead or diseased branches and to shape the tree. Proper pruning encourages healthy growth and fruit production.
Apply a balanced fertilizer in early spring before new growth begins. Avoid over-fertilizing with a nitrogen-rich fertilizer, which can lead to more leaves and fewer fruits.
Thin the fruits in early summer to ensure larger, healthier apples. Leave one apple per cluster, spacing them about 6 inches apart. Macoun apples are typically ready to harvest in late September to October. Pick when the apples are fully colored and the flesh is firm.
Monitor for common apple pests and diseases. Use integrated pest management (IPM) practices. Here is some info on common diseases that affect these trees as well as a typical spray schedule (organic or synthetic).