Avocado trees are commonly grown indoors because they are not cold hardy. While they are a popular indoor plant, there are certainly some limitations to growing them as houseplants. Fortunately, you can grow avocado trees successfully indoors with a few important tips.
Here are ten tips for growing avocado trees indoors (see also ‘6 Indoor trees that enjoy low light (and 6 that much prefer the sun)‘).
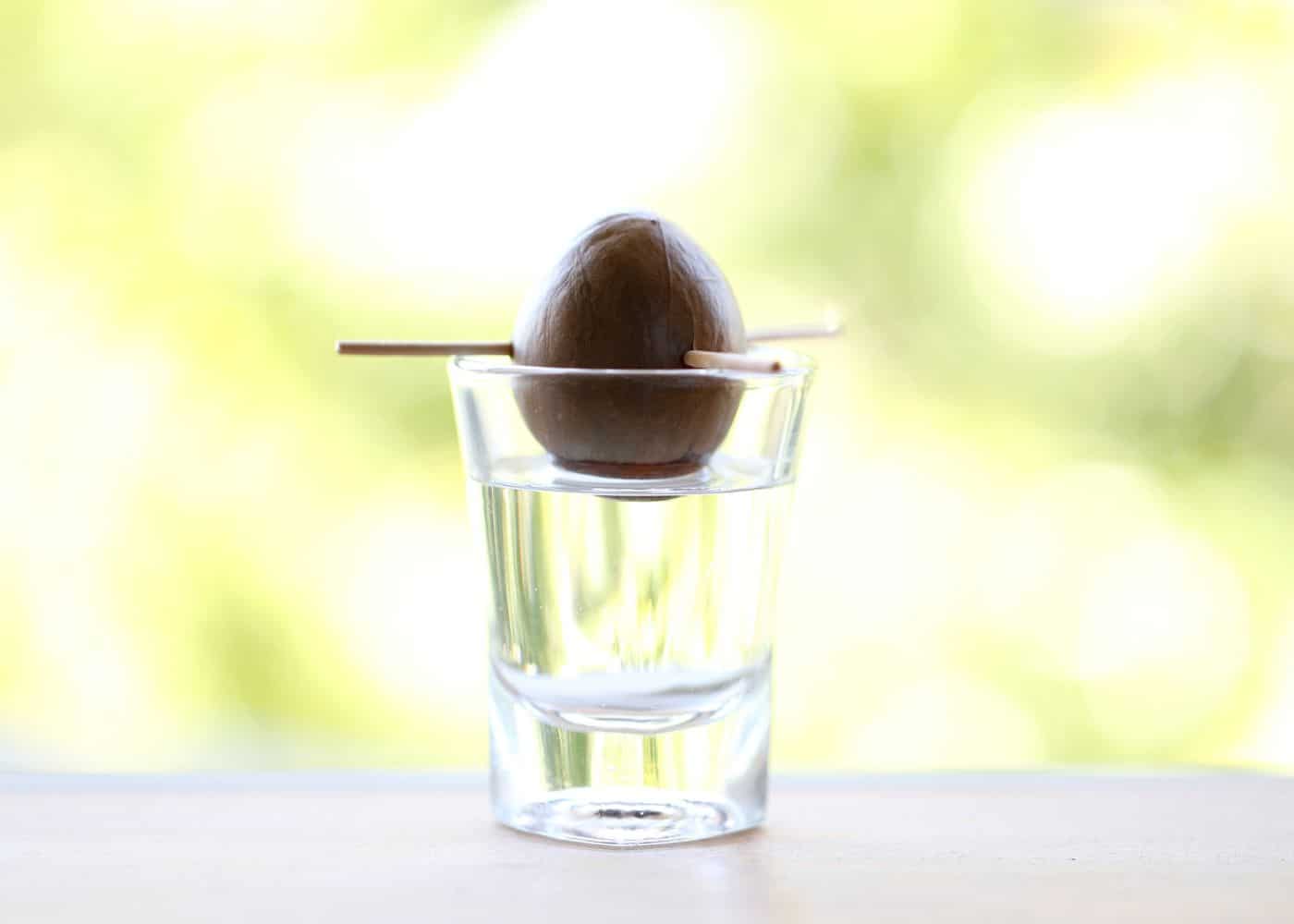

1. Starting from seed is for fun, not for fruit
Starting an avocado tree by sprouting an avocado pit from the grocery store is great fun! It’s a wonderful home project that’s fun for kids and adults alike. That said, this process should be done for the experience, not for the result.
Avocado trees grown from a seed can take 10-15 years to start to produce fruit in good conditions. It is unlikely that the conditions inside your home are as sunny and optimal as conditions would be in their native ecosystem, and so fruiting will be even more delayed.
Secondly, avocadoes do not grow true from seed. You can’t sprout a Hass Avocado pit and expect it to grow a tree that bears similar Hass Avocadoes. For reliable fruit, you need to either graft your own avocado tree or purchase a named cultivar at the nursery. Fifteen years is a long time to take care of a tree just to discover it doesn’t grow tasty fruit!
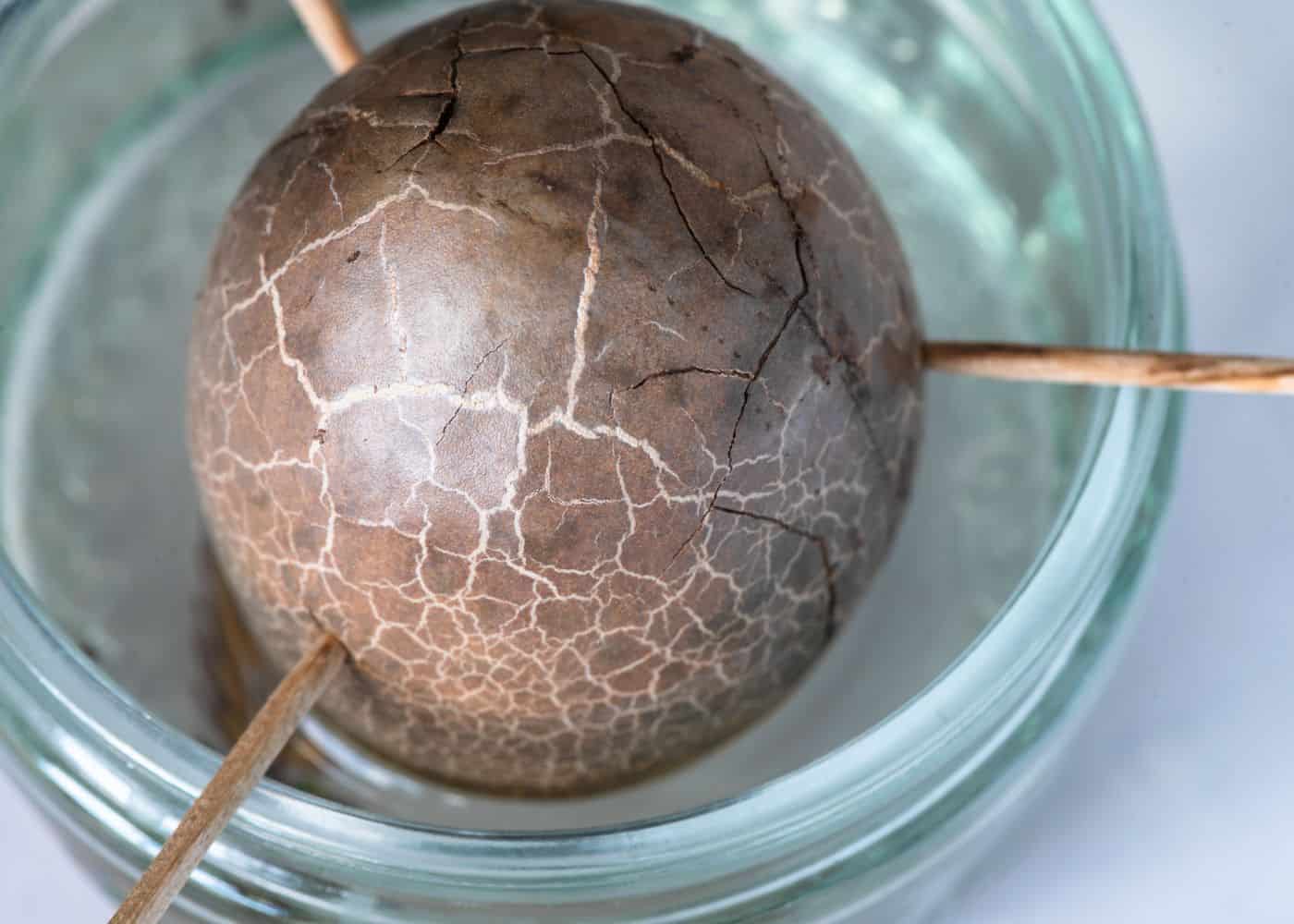

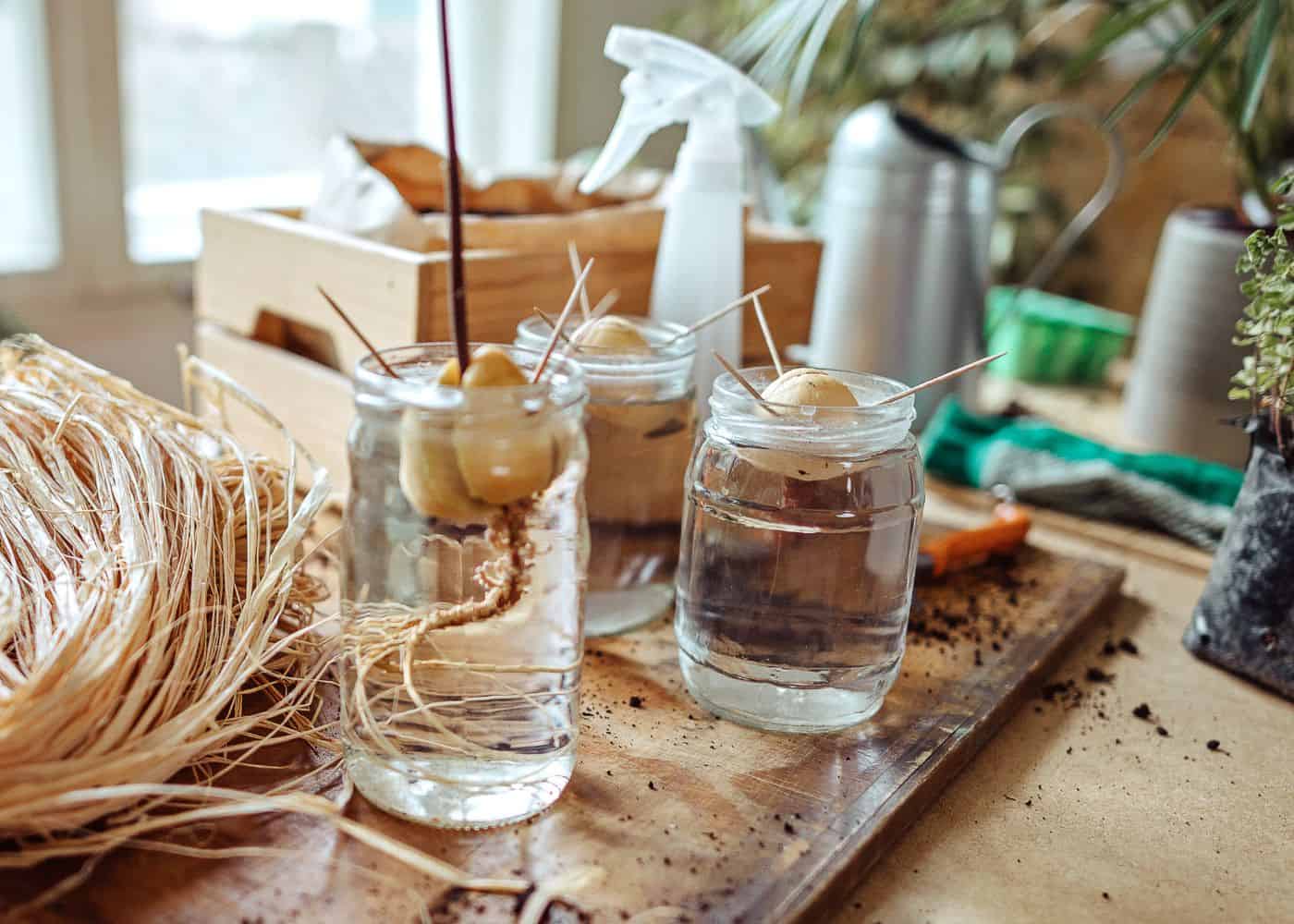
All that said, it certainly can be fun! Here are the basic steps for sprouting an avocado seed:
- Remove the seed from the center of the fruit and gently clean it with water to remove all the debris.
- Stick toothpicks into the sides. Place several toothpicks into the midsection of the avocado. Make sure the toothpicks are fairly evenly spaced around the pit.
- Place the avocado pit partially in the water. Set the broad bottom end of the pit into a glass of water. The broad end is the larger round side of the avocado, and it is where the roots start to sprout. Make sure only about the bottom quarter of the avocado is in the water.
- Add water on a regular basis to keep the water level even. Roots should start to appear within a few weeks to a few months, and you need to maintain the water level in the glass. If roots don’t sprout after several months, throw the seed out and start again with a new one.
- Once the roots grow to two or three inches long, it is time to transplant the seed into potting soil.
“The pit or seed can be sprouted. The result is an interesting and attractive houseplant.
The avocado is actually a tree. It will never produce fruit indoors as it may take 20 or more years to bear fruit.”
Iowa State University
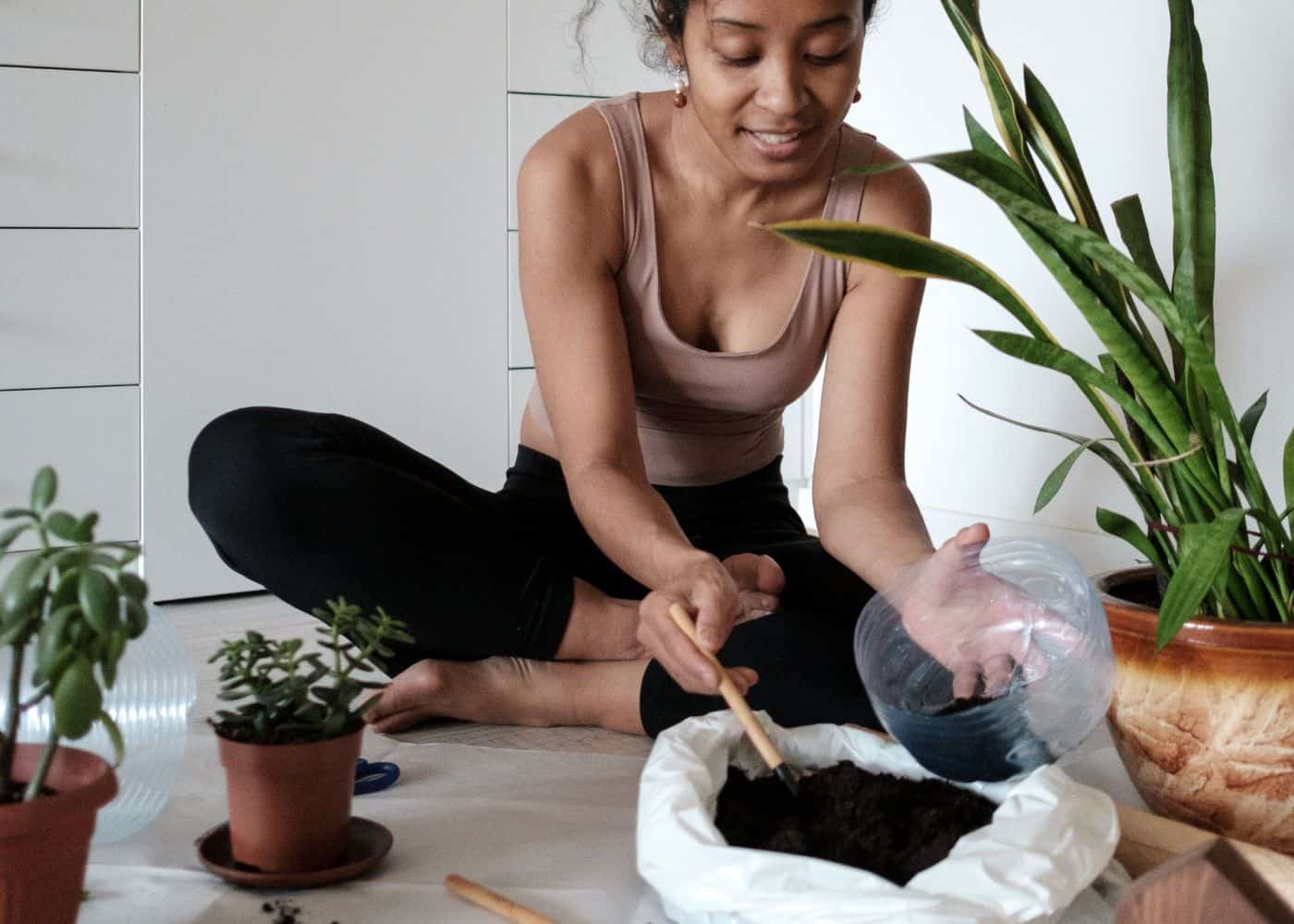

2. Use high-quality potting soil for your avocado tree
If you’re thinking about growing avocado trees, you’ll need to start with the best potting soil possible. While there are many different types of potting soil available, not all of them are well-suited for avocado trees.
When selecting potting soil, look for one that is high in organic matter and has good drainage. Quality potting soil will help your avocado tree to thrive by providing it with the nutrients it needs and promoting healthy root growth. In addition, well-drained potting soil will prevent the roots from becoming waterlogged, leading to problems such as root rot.
Place a bit of the soil into a six to eight-inch planting pot. You should add enough water to the soil to moisten it before transplanting the seed, but make sure not to soak the soil or turn it muddy.
Place the root end of the pit into the pot and gently cover the roots up with soil. The soil should go up high enough to cover most of the seed. You’ll likely want to leave the very top of the seed exposed so you can watch the stem group up and out of it.

3. Avocado trees need lots of light
As soon as they sprout their first leaf, avocado trees require 6-8 hours of direct sunlight to grow well. Indoors, the intensity of the sunlight can be reduced by as much as 90%, and so supplementing with artificial light is a must.
For those of us who don’t live in sunny California, it can be tricky to get our avocado trees to produce fruit. The solution is to grow the trees indoors under plant lights. But with so many different types of plant lights on the market, it can be hard to know which one is best for avocado trees. Here are a few things to keep in mind when choosing a plant light for your indoor avocado tree:
First, consider the intensity of the light. Avocado trees need quite a bit of light to produce fruit, so you’ll want to choose a light with high lumens. Second, think about the color temperature of the light. Avocados prefer a warm climate, so a light with a higher Kelvin rating will be ideal (and also make your home feel less like a bad office building).
“In the United States, avocados are produced commercially in California (65,000 acres),
Texas A&M Agrilife Extension
Florida (6,500 acres), and Hawaii (600 acres).”
4. Avocado plants like warm environments
Avocadoes are heat-loving plants that thrive in warm environments. If you like to keep your house on the cooler end of the thermostat, you may be better off with a different houseplant. Tropical houseplants and small trees tend to grow best at room temperature or warmer, especially during the day (its ok if they are a bit cool at night).
Move the planting pot to an area where the ambient temperature around the pot is ideally in the 65 to 85-degree range. Your avocado tree will likely enjoy the same conditions as an indoor lemon tree.
“Effective but expensive are true greenhouses with climate control capabilities. However, the trees’ size poses challenges for growing them indoors permanently.”
Texas A&M Agrilife Extension

5. Water your tree often
Young trees require water very frequently, especially after transplanting. Newly-transplanted avocado trees are just developing their feeder root network and don’t yet have the capacity to withstand long periods without water. Keep the soil consistently moist for the first six weeks as the plant develops its root system.

6. Watch the air humidity
Avocadoes grow naturally in humid environments like Mexico, Guatemala, and the West Indies. In general, these are environments with humid, warm air, not dry air. This is why large avocados grown indoors are typically grown in climate-controlled greenhouses rather than inside homes.
If you are growing your avocado indoors, try to keep the air humidity at about 40% or greater. This is easiest with a whole-house humidifier or even a one-room standalone humidifier.

7. Fertilize your avocado tree regularly
Trees planted in pots are entirely dependent on gardeners for mineral nutrition. These plants are separated from the outdoor ecosystem that would usually provide food for them, so adding your own fertilizer is a must.
Apply the fertilizer according to the directions on the package about once or twice a month during the spring and summer when the growing cycle is at its strongest to keep the avocado tree strong and healthy.
8. Keep up with pruning your young tree
Once the tree sprouts twigs and branches, you should prune it periodically to help keep the tree healthy and give it a lush, bushy look that helps brighten up a room, especially during the long winter months.
Start pruning when the tree reaches 12 inches tall. Locate the growth node at the top of the tree and cut the tip of the tree off at this point to encourage it to bush out and not get too tall. The growth node is found at the spot where the twigs and branches emerge from the stem.
Cutting the tip off at the growth node helps the tree grow laterally. As the tree grows, you may have to place stakes in the soil to hold up heavy branches.

9. Have patience
Patience is a virtue when growing avocado trees. Avocado trees, when grown indoors, often take years before they actually produce fruit you can eat. While grafted trees produce fruit years before seedling trees, it can still feel like a long wait. It may take a decade for a grafted tree to start to produce fruit, even in good conditions.
Avocadoes also take a long time to grow from blossoms into ripe fruit. Mexican avocadoes are the quickest at about 6 months to develop on the tree, while Guatemalan avocadoes can take over a year to grow to size!
Also, note that avocados do not fully ripen on the tree. Once the fruit is produced, you’ll need to pluck an avocado off the tree and let it sit for a couple of days. If it doesn’t soften up after a couple of days, the fruit isn’t ready to be picked. However, once it softens or shrinks up after sitting on the counter for a couple of days, the tree is ready for plucking.
“Do not grow seedlings from supermarket avocados, for several reasons: Avocados do not come true from seed; ungrafted seedlings may take up to 10 to 15 years to bear fruit; and salty irrigation water can cause moderate to severe leaf tip burn on these plants.”
Texas A&M Agrilife Extension

10. Understand that your tree may never produce fruit
Indoor avocado trees are grown mainly as interesting foliage houseplants. They are not intended to grow fruit. These trees take too long to grow and grow too large to make decent houseplants.
To grow a fruiting avocado tree indoors, your best bet would be a large, climate-controlled greenhouse equipped with proper equipment for irrigation, lighting, and air humidity. An avocado tree grown in ambient light inside a home is unlikely to thrive for the years required for it to start to fruit. It will also lack the pollination partners and insects of outdoor conditions.
“Avocado plants grow rapidly. They often have to be discarded after 2 or 3 years because they’ve become too large for indoors.”
Iowa State University

FAQs
How do you care for an indoor avocado plant?
Basic care for indoor avocado plants includes providing it with a bright plant light, watering it whenever the top inch or two of soil dries out, fertilizing it during the growing season, and acting quickly to deter any pests you observe.
Is an avocado plant indoor or outdoor?
Avocado plants are outdoor plants, but you can usually grow them indoors for several years before they outgrow their space. Avocado trees really like to be outdoors once they are 2-3 years old, but you could grow them inside a large climate-controlled greenhouse too.
Can an indoor avocado plant bear fruit?
An indoor avocado plant is very unlikely to bear fruit. For an indoor avocado tree to bear fruit, it would need a large climate-controlled growing space, pollination partner varieties, and artificial blossom pollination. You would also be best to grow named grafted cultivars, not seedling plants.
Resources
References
- University of California, Avocado Handbook
- Iowa State University, Sprouting an Avocado Seed
- Texas A&M Agrilife Extension, Texas Fruit and Nut Production: Avocadoes
All about growing avocadoes
Avocado trees are surprisingly easy to grow if you live in a warm climate. And if you live somewhere with cold winters, you can usually keep baby trees indoors for a couple of years.