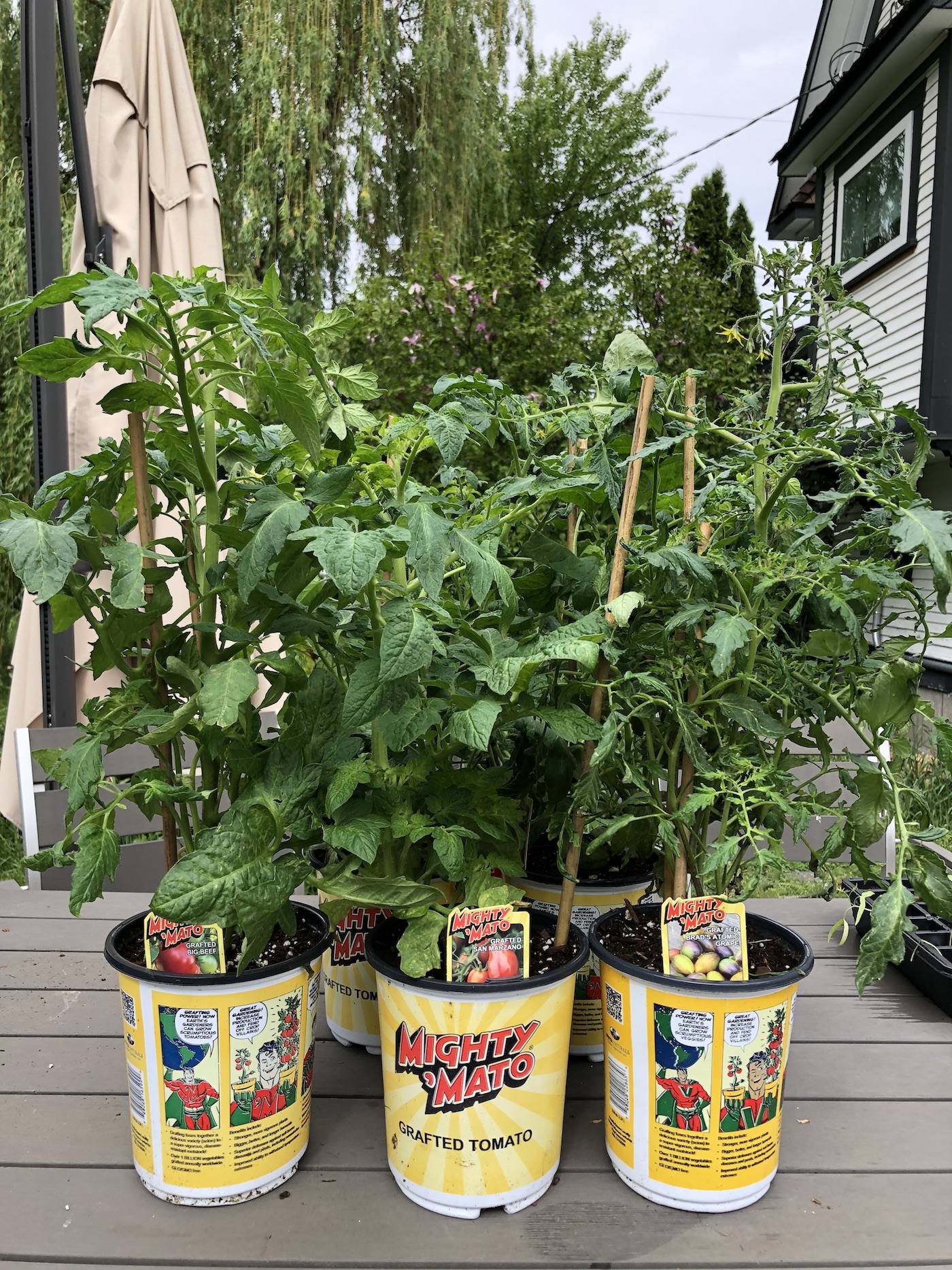
Grafted tomato plants are the hottest thing in homegrown tomato tech these days! But how do you grow these handcrafted plants?
Grafted tomato plants are created by attaching the aboveground portion of one tomato variety with the belowground portion of a different variety. The top part of the plant (the scion) is typically from a specialty tasty variety. The roots of the plant (the rootstock) is chosen from a different variety bred specifically for vigorous growth and resistance to common tomato diseases. Each plant is created by hand. In the garden, a grafted tomato plant needs to be planted with the graft union joint above the soil line.
Read on to learn all about grafted tomato plants!
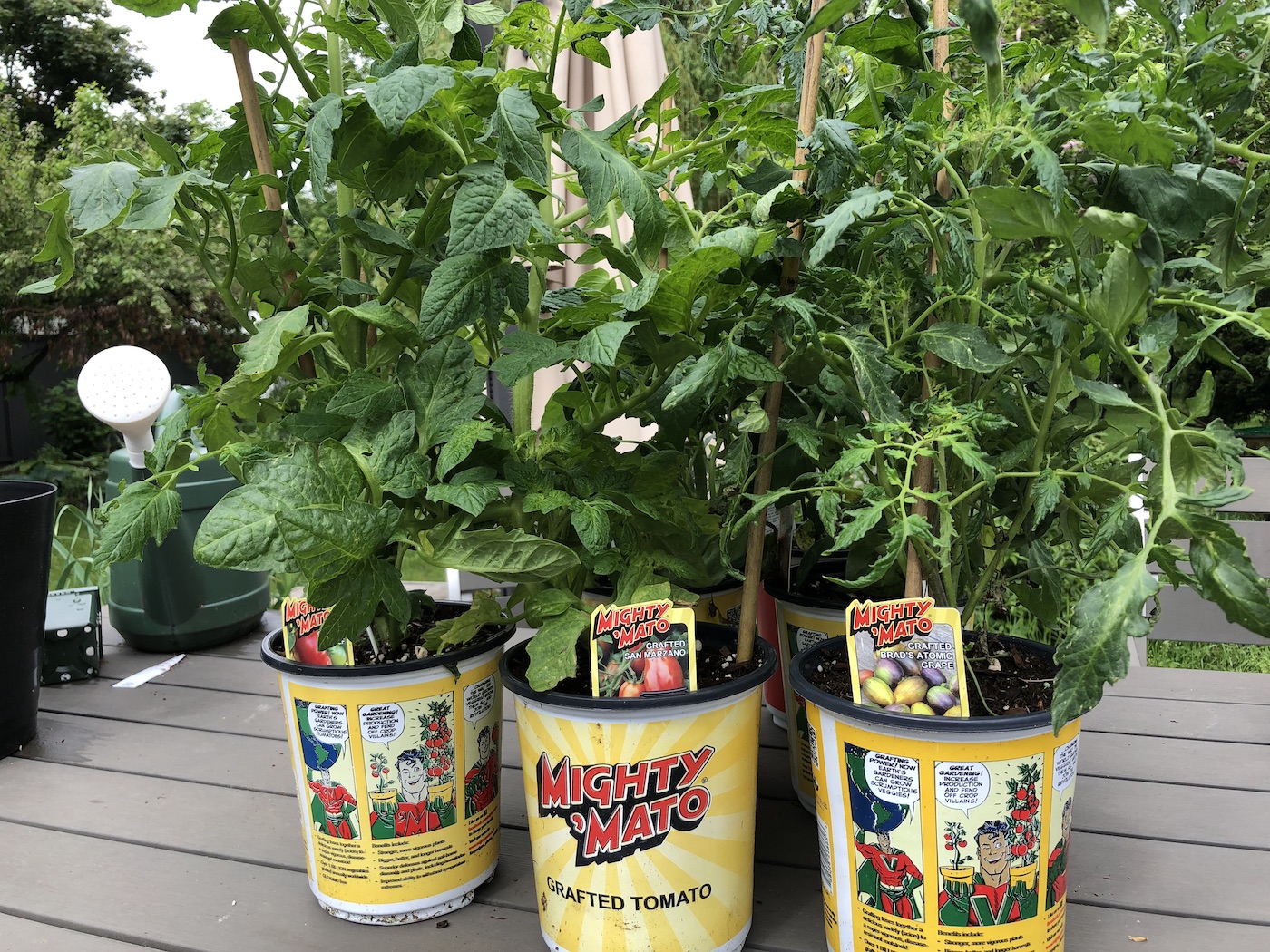

Introduction to grafted tomato plants
If you’re like most home gardeners, you’re always looking for ways to improve your yields and get the most out of your plants. One trick that can help is grafted tomatoes. Grafting is a process where you connect two different plants together so that they share the same root system. This can be a great way to get more tomatoes from your heirloom plants, or even to create hardier hybrids.
Grafted tomato plants are created by taking a cutting from a desirable plant and grafting it onto the rootstock of a stronger plant. This can be done with many different types of plants (like different types of apples), but tomatoes are one of the most popular vegetables to graft.
Grafting allows you to take advantage of the best qualities of both tomato plants. For example, you could graft a disease-resistant rootstock onto the stem of a delicious heirloom tomato. This would give you a plant that is both disease-resistant and full of flavor.
Buying grafted tomato plants
Grafted tomato plants are most common in Japan and the Netherlands, but are becoming easier to find in North America. One of the most popular brands of grafted tomatoes is the “Mighty ‘Mato” brand from Super Naturals Grafted Plants. Grafted tomato plants are now available for purchase at specialty nurseries all around the world.
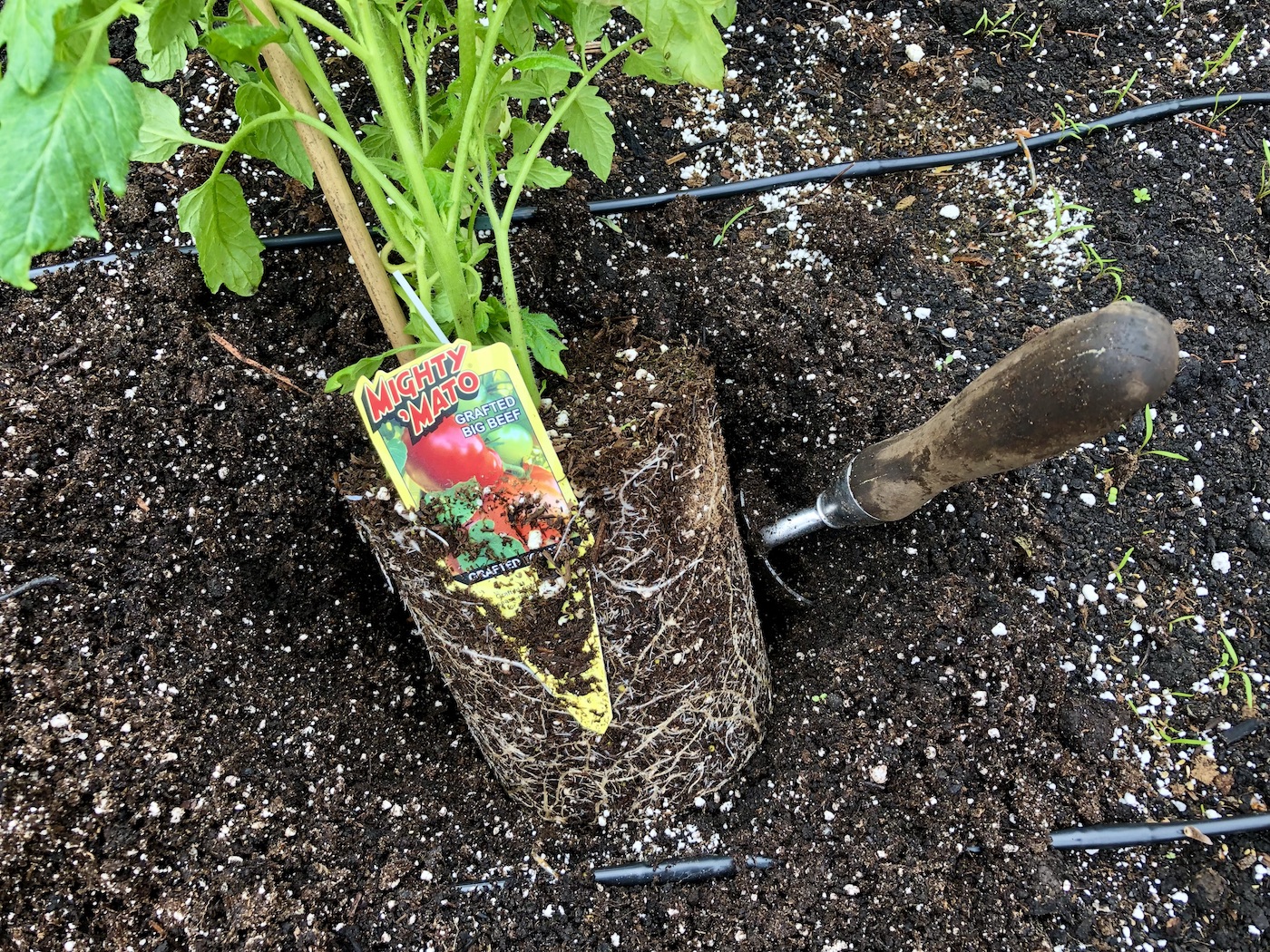

Planting grafted tomato plants
Grafted tomato plants need to be planted with the graft union joint above the soil. This is so the aboveground scion portion is unable to root into the soil. Most gardeners plant seedling tomato plants in the garden at about 4-6 inches deeper than the seedling pot, but this is not the case for grafted tomato plants (with the only exception being the grafted pomato plant).
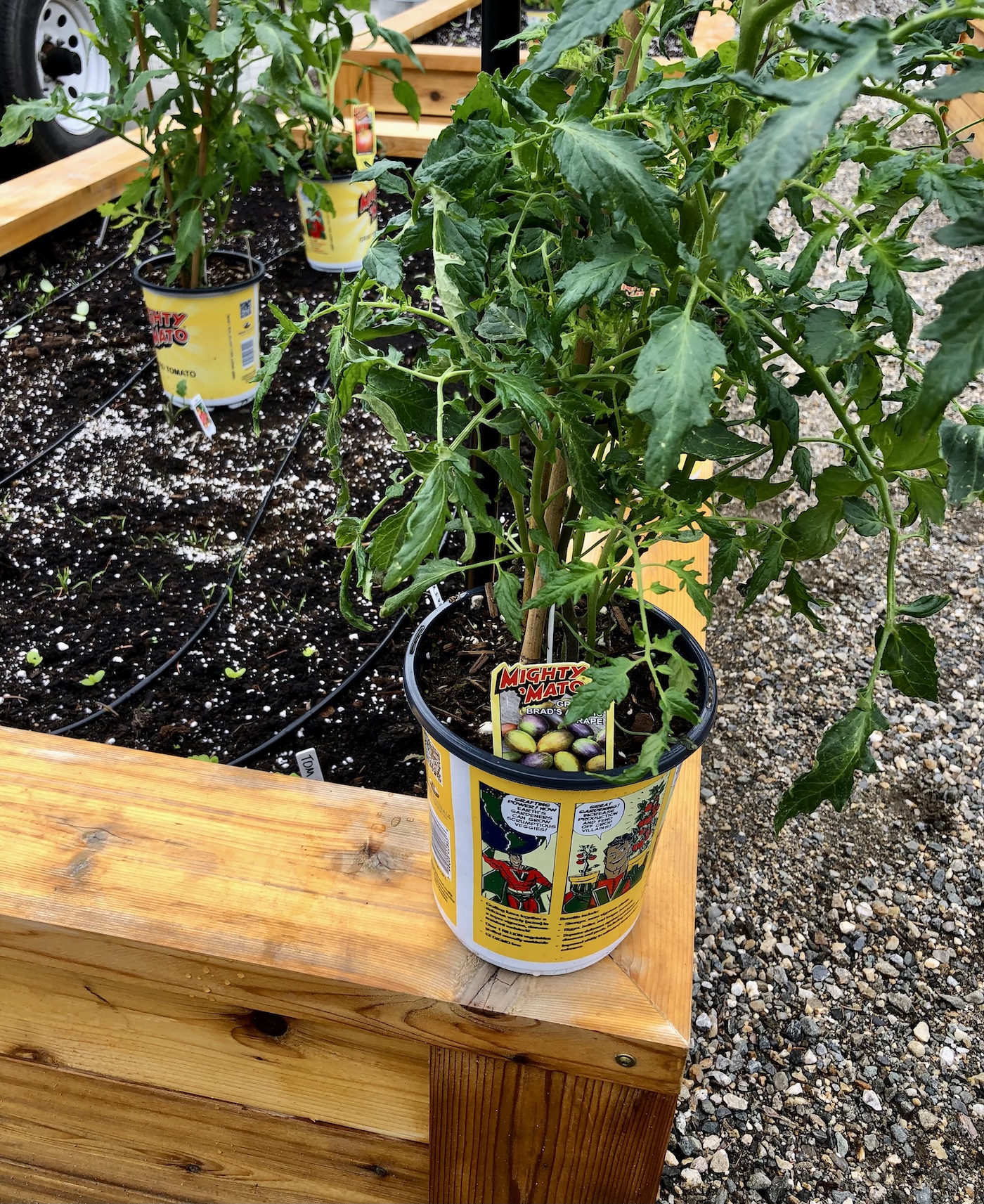

Growing grafted tomato plants
Grafted tomatoes can be grown just like growing a regular seed-grown tomato plant. Be sure to use well-drained soil and provide a heavy-duty tomato cage.
Harvesting grafted tomato plants
Grafted tomato plants will usually produce fruit earlier than seed-grown tomato plants. When harvesting, be sure to cut the stem rather than pull the fruit off the plant. This will help avoid damaging the plant.
How to graft tomato plants
The process of grafting tomato plants is not difficult, but it does require some care and attention. It can be a fun experiment for gardeners looking to add vegetable grafting skills to their personal toolkit!
Here are the basic steps for grafting tomato plants:
1. Choose the rootstock. This should be a strong, healthy rootstock plant that is resistant to common soilborne diseases and pests. Most rootstocks are also bred for nutrient uptake and vigorous growth. Popular rootstock plants include Fortamino and Estimino.
2. Choose the scion. This is the plant that you want to graft onto the rootstock. The scion plant should be a healthy plant with desirable qualities (like disease resistance or flavor). Popular scion plants include heirlooms like Brandywine and San Marzano, as well as modern open-pollinated varieties like Brad’s Atomic Grape. The rootstock and scion should have a similar diameter for a compatible graft union.
3. Make a clean cut on the rootstock below the cotyledons (first baby leaves). Cut off the top of the rootstock at a 45-degree angle using a sharp razor.
4. Make a clean cut on the scion. Cut off the bottom of the scion at a 45-degree angle.
5. Match up the cuts and tie them together. The two cuts should fit together snugly. Use grafting tape or a rubber band to tie them together. You can also use a specialty grafting tube or grafting clip to hold the spliced pieces together.
6. Graft up a few more grafted plants. Grafted tomatoes aren’t always successful, and so it makes sense to graft extra plants just in case one doesn’t work out.
7. Put the newly grafted plants in a warm, humid place. A propagation dome or plastic bag can create the ideal environment for the graft to heal.
8. Wait for the graft to take. This can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. Once the graft has taken, you can remove the propagation dome or plastic bag.
9. Care for your plant. Water regularly and fertilize as needed.
10. Enjoy your grafted tomato plant!
Grafting tomato plants is a great way to improve your yields and create hardier hybrids. With a little care and attention, you can graft your own plants at home.
“The primary motivation for grafting tomato has been to prevent the damage caused by soilborne pathogens under intensive production system. However, recent reports suggest that grafting onto suitable rootstocks can also alleviate the adverse effects of abiotic stresses such as salinity, water, temperature, and heavy metals besides enhancing the efficiency of water and nutrient use of tomato plants.”
Tomato Grafting: A Global Perspective, Nov 2017, by Hira Singh, Pradeep Kumar, Sushila Chaudhari, and Menahem Edelstein

Types of grafting
There are several specialty grafting methods that can be used for grafting tomatoes. The most popular methods include tube grafting and cleft grafting.
Tube grafting, also known as splice grafting, top grafting, or Japanese top grafting, is a type of grafting that uses a hollow tube to join the rootstock and scion. This method is often used for grafting delicate plants like tomatoes. You can sometimes see the tube or stake for the clip remaining at the base of the plant when you purchase a grafted tomato.
Cleft grafting is a type of grafting that involves making a clean cut on the rootstock and then inserting the scion into the cut. This method is often used for larger rootstocks paired with skinny scion pieces. Cleft grafting for tomatoes is not as common as tube grafting.